The sustainability of galvanized steel
Galvanized steel is an integral part of everyday life and is all around us. But how does its prevalence today affect the environment of the future? How sustainable is it? What role does it play in the circular economy? And is the galvanizing process itself environmentally friendly?
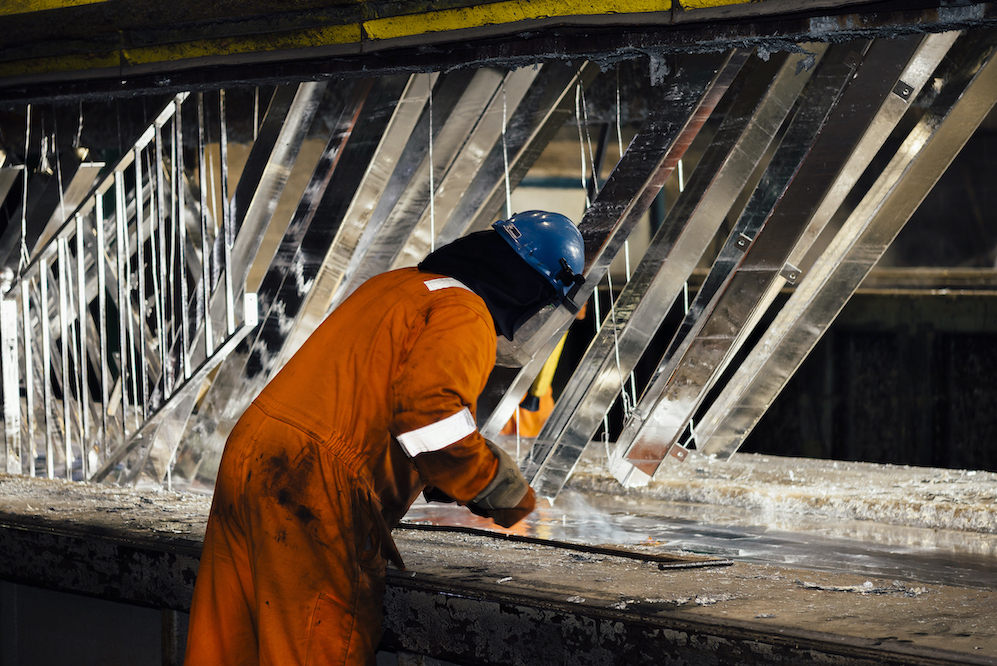

Steel is essential for housing, infrastructure, transport, manufacturing, and agriculture. Used as frames for our buildings, safety on our roads, and support for the bridges we cross, we must never waste the resources used to produce it by throwing it away when the original function is no longer valid. Instead, we must repurpose steel, especially if the world wants to move away from traditional business models of use-throw-away-remake to a more environmentally friendly, sustainable circular economy that aims to eliminate waste and repurpose resources.
What is a circular economy and how can galvanizing play a part?
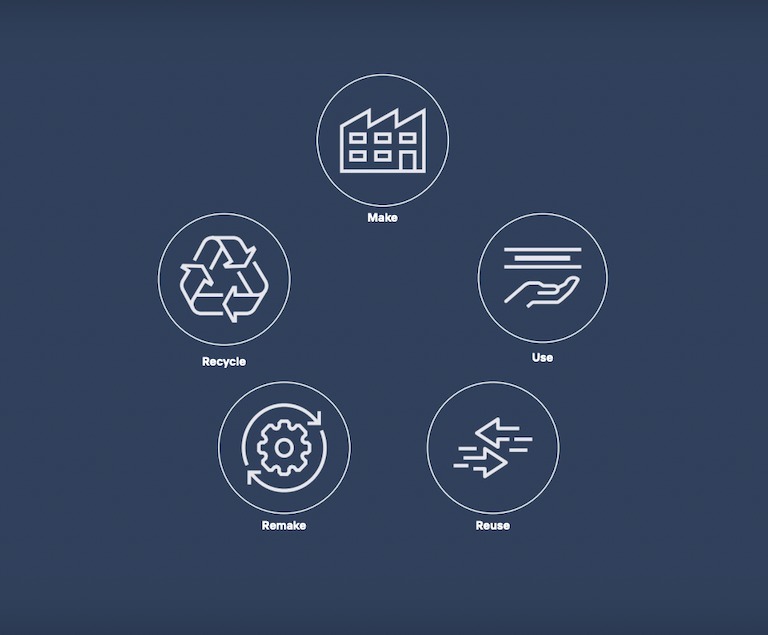
A circular economy encourages materials to be made, used, reused, remade, and recycled.
Hot dip galvanizing fits perfectly into a circular economy because it optimises the durability of steel (enabling it to be used again) and facilitates the ease of reuse. It can be recycled if there’s no immediate need to repurpose it. Here’s how:
Optimising durability
When steel is galvanized, it is immersed in a bath of molten zinc, where it alloys with the iron in the steel to form zinc/iron alloy layers. These layers form the basis of the coating, which is covered with free zinc as the steel lifts from the galvanizing bath. The result is a robust, durable, corrosion-protective finish that will last many years.
Without a galvanized coating, steel would corrode, and its lifespan would be short. However, with a galvanized coating, steel can last between 34 and 170 years before the base steel is exposed. This means that steel can be used for the original purpose for which it was fabricated, and – once the project is dismantled – the steel is still good enough to be used elsewhere.
Facilitating ease of reuse
Once a structure – such as a house or fencing – reaches its end of life, the steel can easily be repurposed if it has been hot dip galvanized. The galvanized coating protects the steel from impact and abrasion when disassembled and reassembled.
Recycling
Finally, galvanized steel fits nicely into a circular economy because it can be melted and used repeatedly without losing quality if there is no immediate need for repurposing.
The zinc coating can also be reused. Zinc and steel are recycled in well-established steel recycling processes. The zinc particulates are returned, without loss of properties, to zinc production plants, where they are incorporated into zinc ingots and reused in the galvanizing process.
How else does the galvanizing process enhance sustainability?

A hot dip galvanized finish gives steel a long life and durability. In addition, it creates a maintenance-free finish, which lessens the carbon emissions usually associated with the upkeep of non-galvanized steel.
Mick Jackson from the Joseph Ash Group (Premier Galvanizing’s parent company) says: “Imagine a bridge made from non-galvanized steel. It would need maintenance every year to protect it from rust and corrosion. It would also need repainting at regular intervals. This requires paint, a workforce, transport for the workers and a means to protect the land or water below from paint contamination. This maintenance is not required if the same bridge is made from galvanized steel, therefore carbon emissions are greatly lessened.”
Is the galvanizing process environmentally friendly?
Galvanizing plants are self-contained, with steel going in at one end and the final product coming out at the other.
Modern galvanizing plants also use zinc very efficiently throughout the galvanizing process. For example, excess metal from the dipping process deposits back into the galvanizing bath. Zinc that oxidises on the surface is removed as ash and recycled, and dross from the bottom of the bath is routinely removed and has a high recycling value.
Other process consumables, such as hydrochloric acid and flux solutions, have important recycling or regeneration routes. Spent hydrochloric acid solutions are used to produce iron chloride for treating municipal wastewater, for example. Closed-loop flux recycling is also used in many plants, and improved monitoring and maintenance of flux tanks reduce the volume of solids for disposal. Compared to other coating technologies galvanizing uses low volumes of water, with plants rarely discharging wastewater. Any wastewater generated can be treated and reused, with only small volumes of stable solids requiring external disposal.
While not considered a particularly energy-intensive sector, the galvanizing industry also has set targets for energy efficiency and improved energy management. New technology has seen improvements in burner efficiency, bath lid efficiency, and reuse of waste heat to warm pre-treatment tanks. Plant emissions are also carefully controlled to ensure neighbouring communities are not adversely affected.
A strong commitment to the circular economy
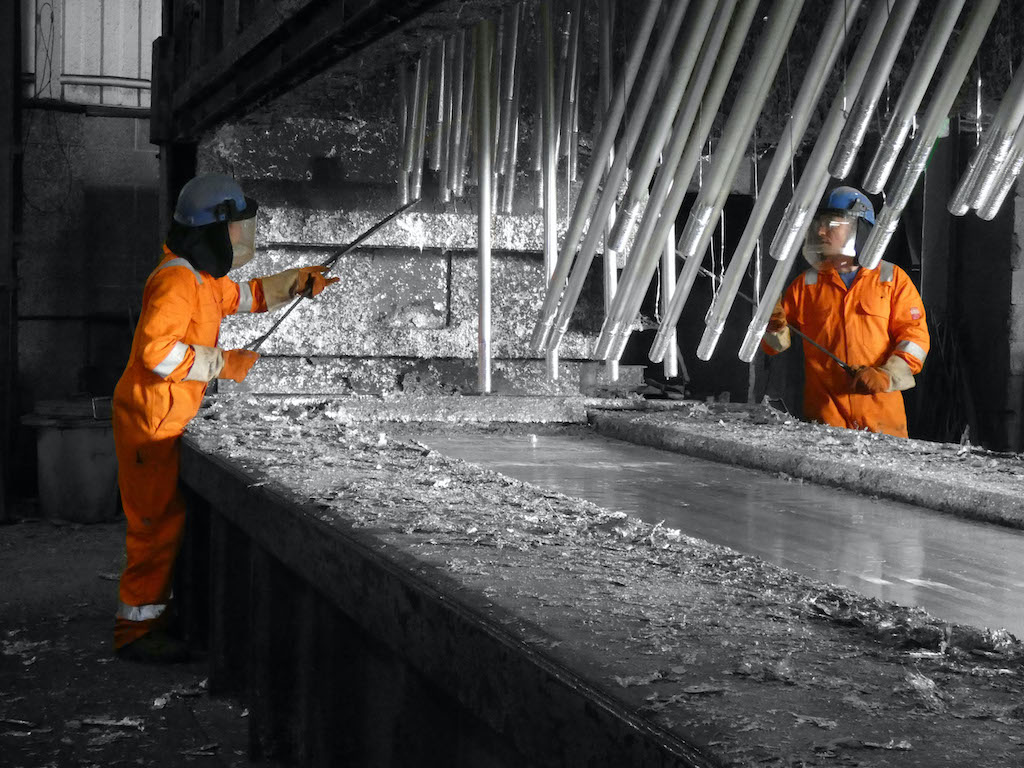

Steven Hopkins, Managing Director at the Joseph Ash Group, said: “We count ourselves fortunate to be involved with such a sustainable product, playing, as it does, a critical role in extending the life of steel structures by decades. In addition, reducing our environmental impact has been close to our hearts for many years, hence our heavy investment in fume capture and recycling by-products.”
We firmly believe in a circular economy, where the needs of present-day society are met, without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.”
Please get in touch to find out more about galvanized steel or the sustainability processes at Premier Galvanizing.
You can view the new EGGA guide – ‘Galvanized Steel and Sustainable Construction: Solutions for a Circular Economy’ here.
Next page